Biometrics
Height
183.7
cm
Weight
81.5
kg
BMI
24.15
kg/m^2
Systolic Blood Pressure
115
mmHg
Optimal
Diastolic Blood Pressure
73
mmHg
Optimal
Pulse
68
bpm
Cholesterol panel
Apolipoprotein B (apoB)
1.2
g/L
Very High
Total cholesterol
6.79
mmol/L
High
HDL-cholesterol
1.71
mmol/L
Optimal
LDL-Cholesterol
4.92
mmol/L
High
TG:HDL-C ratio
0.47
Optimal
Triglycerides
0.35
mmol/L
Optimal
Lipoprotein(a) (mg/dL)
17.7
mg/dL
Low Risk
Metabolic profile
Fasting insulin
1.6
mIU/L
Optimal
Fasting glucose
4.4
mmol/L
Optimal
HbA1c
5.8
%
Average
HOMA-IR
0.31
Optimal
Estimated Average Glucose (eAG)
6.65
mmol/L
Uric acid
284.44
µmol/L
Optimal
Blood profile
Haemoglobin
13.2
g/dL
Low
Red cell count
4.6
x 10^12/L
Low
Haematocrit
41
%
Low
MCV (Mean corpuscular volume)
90
fL
Optimal
MCH (Mean corpuscular haemoglobin)
29
pg
Optimal
MCHC (Mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration)
32
g/dL
Optimal
RDW (red cell distribution width)
12.6
%
Optimal
Platelets
213
x 10^9/L
Optimal
Mean Platelet Volume (MPV)
7.1
fL
Optimal
Total White Cell Count (TWC)
5.2
x 10^9/L
Optimal
Neutrophils
2.37
x 10^9/L
Optimal
Lymphocytes
2.27
x 10^9/L
Optimal
Monocytes
0.39
x 10^9/L
Optimal
Eosinophils
0.11
x 10^9/L
Optimal
Basophils
0.06
x 10^9/L
Optimal
Neutrophil %
45.5
%
Optimal
Lymphocytes %
43.7
%
Optimal
Monocytes %
7.5
%
High
Eosinophils %
2.1
%
Optimal
Basophils %
1.2
%
High
Inflammation panel
High-sensitivity C-reactive Protein (hsCRP)
0.3
mg/L
Optimal
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
3
mm/hr
Optimal
Rheumatoid factor (RF)
15
IU/mL
Optimal
Liver function
Alanine transaminase (ALT)
25
U/L
Optimal
Aspartate transaminase (AST)
33
U/L
Optimal
Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT)
25
U/L
Optimal
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
54
U/L
Optimal
Total bilirubin
9
µmol/L
Optimal
Total protein
75
g/L
Optimal
Albumin
44
g/L
Optimal
Globulin
31
g/L
Optimal
Albumin/Globulin Ratio
1.42
Optimal
Hepatitis Bs Antigen
Non-reactive
Positive
Hepatitis Bs Antibody
2.5
IU/L
Low
Hepatitis C Antibody
Non-reactive
Positive
Fibrosis-4 Index (FIB-4)
1.02
Optimal
Kidney profile
Cystatin C
0.79
mg/L
Optimal
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Creatinine-CystatinC (eGFRcr-cys)
110.1
mL/min/1.73m2
Optimal
Creatinine
92
µmol/L
Optimal
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Creatinine (eGFRcr)
94
mL/min/1.73m2
Optimal
BUN (Urea)
4.1
mmol/L
Optimal
Sodium
137
mmol/L
Typical
Potassium
3.9
mmol/L
Typical
Chloride
104
mmol/L
Typical
Carbon Dioxide (Bicarbonate)
22
mmol/L
Optimal
Urine creatinine random
14.1
mmol/L
Urine microalbumin random
5
mg/L
BUN/Creatinine Ratio
11.04
Average
Vitamins and minerals
Vitamin D
37
ng/mL
Typical
Folate (Vitamin B9)
29.6
nmol/L
Optimal
Vitamin B12
415
pmol/L
Optimal
Homocysteine
7
µmol/L
Optimal
Calcium
2.25
mmol/L
Typical
Magnesium
0.83
mmol/L
Optimal
Phosphate
1.1
mmol/L
Typical
Iron
17.6
µmol/L
Optimal
Iron Saturation
34
%
Optimal
Total Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC)
52.2
µmol/L
Optimal
Ferritin
210
ng/mL
Optimal
Omega-3 Index
6
%
Average
Corrected Calcium
2.17
mmol/L
Typical
Hormone panel
Free Thyroxine (T4)
12.1
pmol/L
Optimal
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
1.19
mIU/L
Optimal
Free Testosterone
500
pmol/L
High
Total testosterone
29
nmol/L
Optimal
Estradiol
118
pmol/L
Optimal
Luteinising Hormone (LH)
4.15
IU/L
Typical
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
4.3
IU/L
Typical
Sex Hormone Binding Globulin (SHBG)
51.6
nmol/L
Typical
Cortisol
375.8
nmol/L
Typical
DHEA-S
8.5
µmol/L
Optimal
Cortisol:DHEA-S ratio
0.044
Optimal
Insulin-like Growth Factor 1
162.6
ng/mL
Optimal
Free Testosterone:Cortisol ratio
1.33
Optimal
Cancer screening
Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT)
Negative
Optimal
Prostate specific antigen (PSA), Total
0.82
µg/L
Optimal
Alpha Fetoprotein (AFP)
5.2
µg/L
Optimal
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
1.7
µg/L
Optimal
CA 19-9
5
U/mL
Optimal
Urine analysis
Urine colour
Yellow
Urine clarity
Clear
Urine pH
7
Optimal
Urine specific gravity
1.02
Optimal
Urine white blood cells (cells/µL)
0
cells/µL
Optimal
Urine red blood cells (cells/µL)
0
cells/µL
Optimal
Urine epithelial cells (cells/µL)
0
cells/µL
Optimal
Urine nitrite
Negative
Optimal
Urine protein
Negative
Optimal
Urine glucose
Negative
Optimal
Urine ketones
Negative
Optimal
Urine urobilinogen
Negative
Optimal
Urine bilirubin
Negative
Optimal
Urine leukocytes
Negative
Optimal
Urine erythrocytes
Negative
Optimal
Urine casts
Nil
Optimal
Urine crystals
Nil
Optimal
Urine bacteria
Nil
Optimal
Urine yeasts
Nil
Optimal
Systolic Blood Pressure
115
mmHg
Optimal
•
Sep 2024
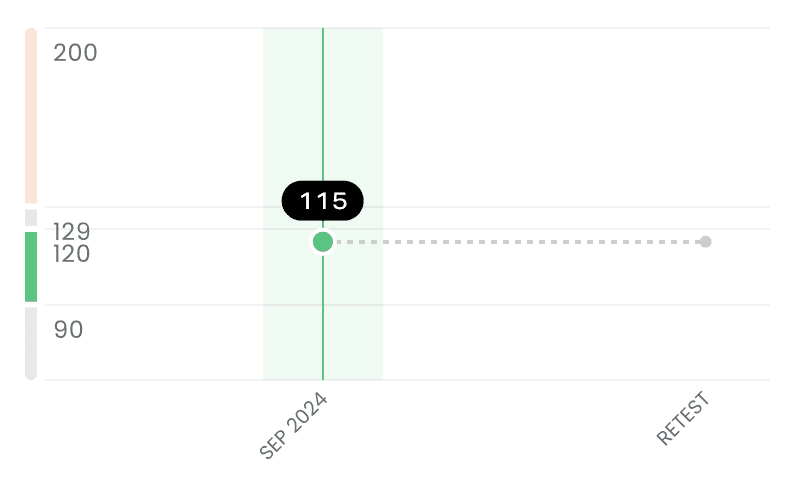
Systolic pressure refers to the maximum pressure within the large arteries when the heart muscle contracts to pump blood through the body.
Blood pressure is tightly controlled in our body to maintain a level high enough to supply our organs, but not so high as to cause damage. It is primarily affected by our heart and blood vessel function. Blood pressures rise and fall throughout the day, but when blood pressure remains high for an extended time, it can eventually cause a number of serious complications, including heart disease, stroke and kidney damage, among others.